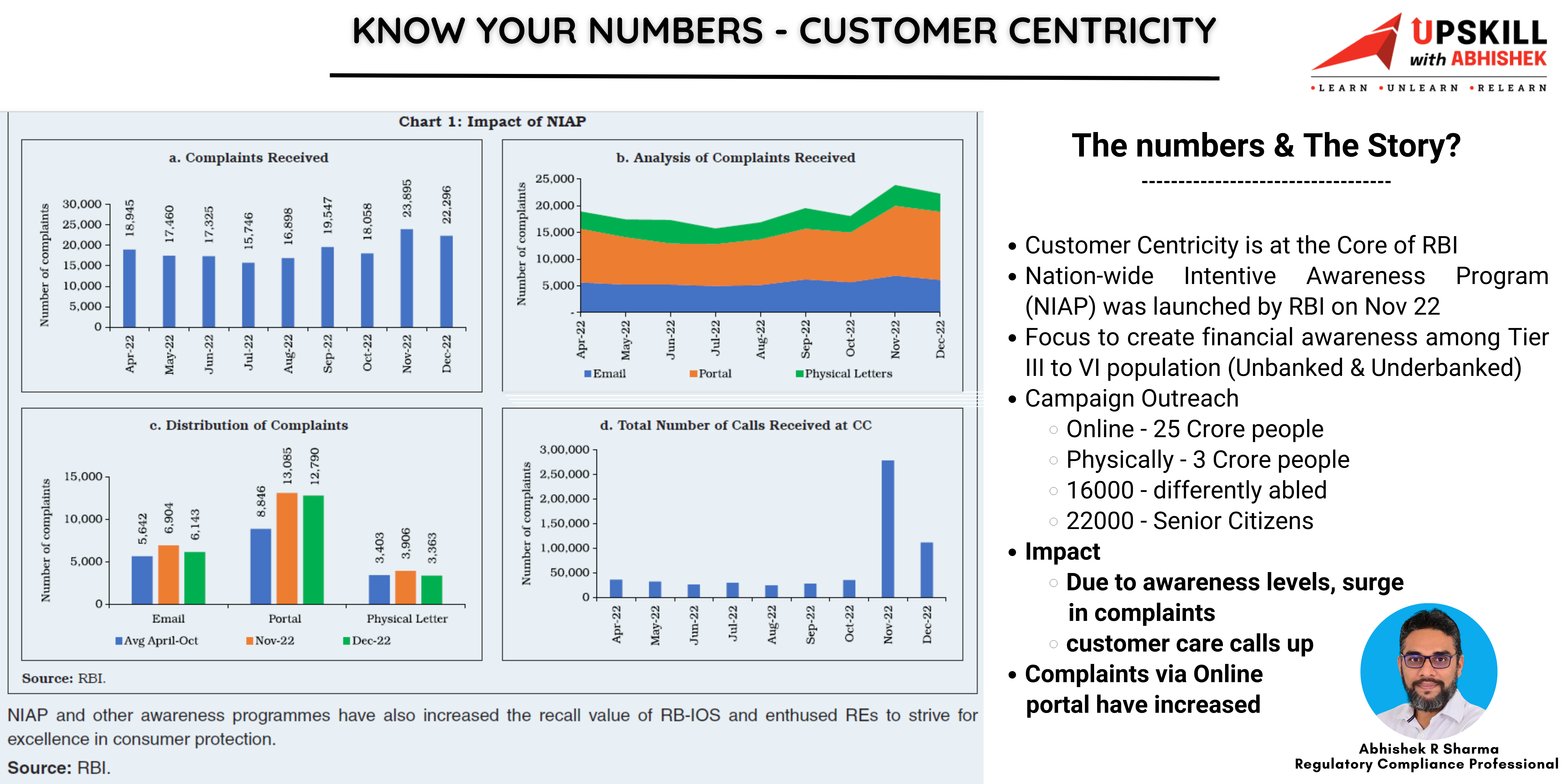
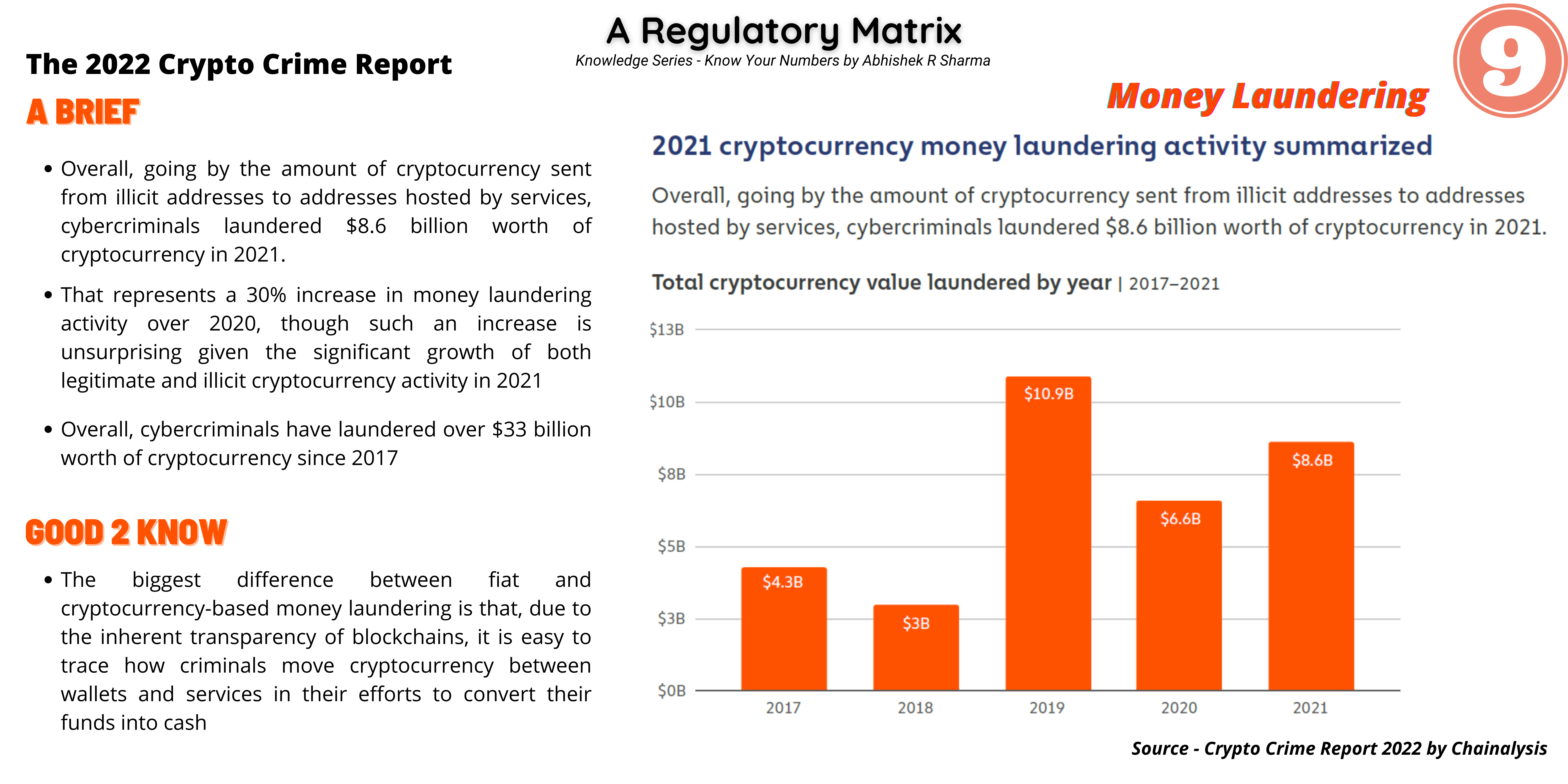
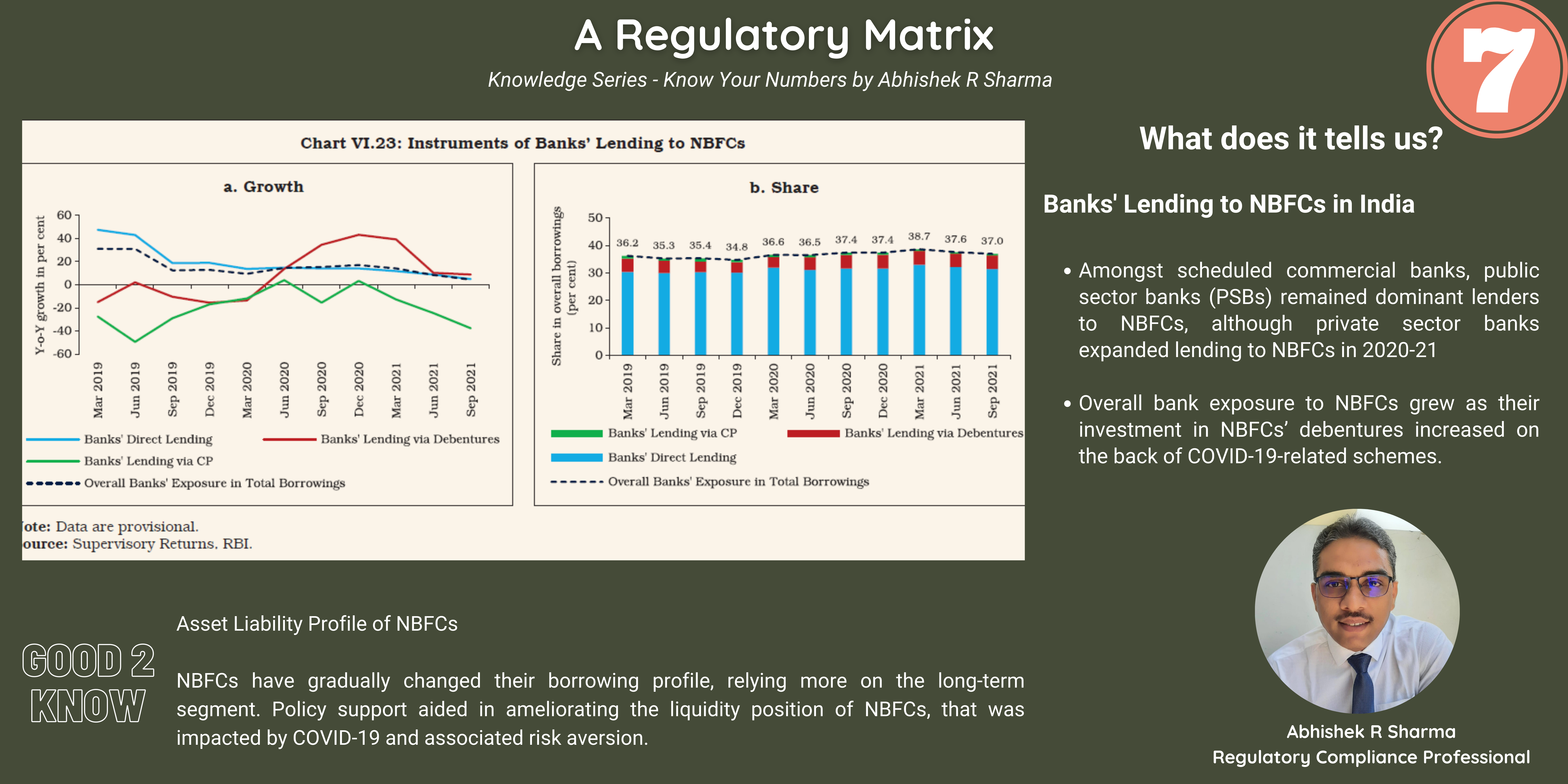
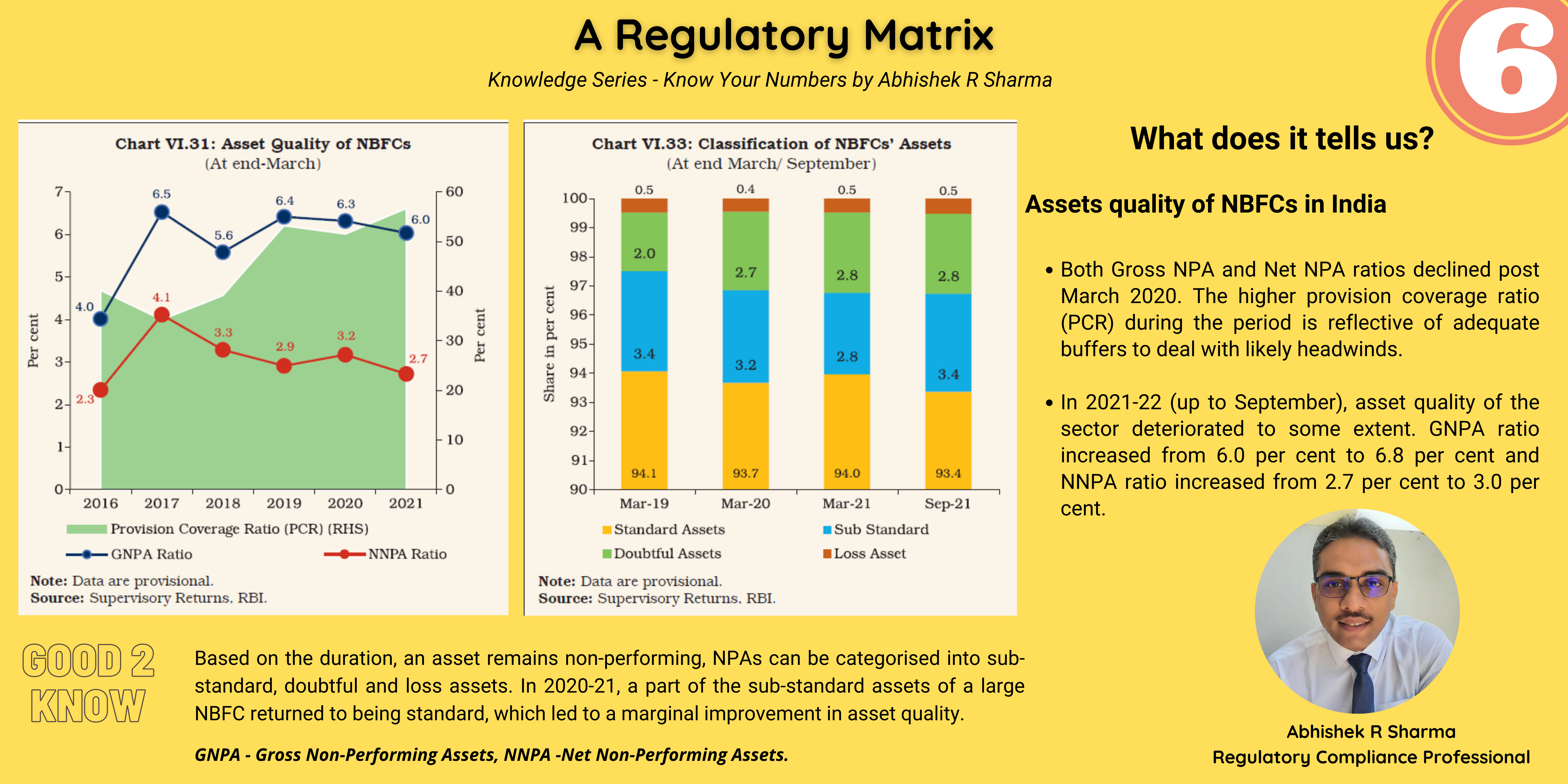
- India is categorized as a ‘leader’ or ‘strong’ in respect of 25 (21 in the previous exercise) out of 40 indicators and
- Categorized as ‘weak’ in respect of 8 (12 in the previous exercise) indicators.
- Significant progress and moved to a leadership position in large value payment systems and fast payment systems, which contributed to rapid growth in digital payments.
- The exercise highlights that there is scope for improvement in acceptance infrastructure i.e. ATMs and PoS terminals.
Benchmarking India’s Payment Systems